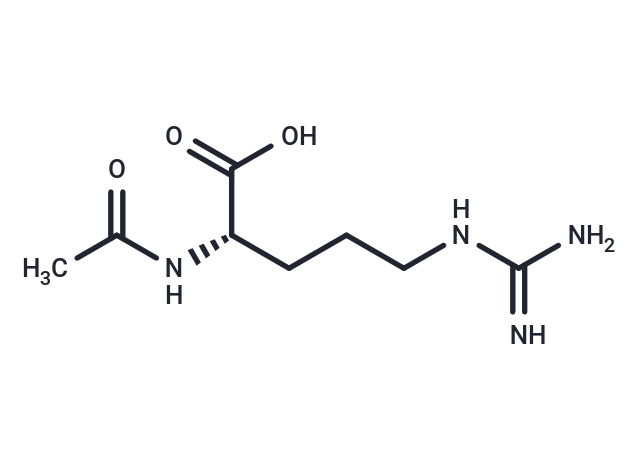
| N-Acetyl-L-arginine (Ac-Arg-OH), an N-acyl-L-alpha-amino acid with a strong basic nature (based on its pKa), has elevated serum levels in hyperargininemic patients and is associated with several diseases, including uremia and colorectal cancer. In untreated hyperargininemic patients, it reaches its highest levels in cerebrospinal fluid. It has also been detected in apples and loquats, suggesting it could be a potential biomarker for consumption of these foods. Additionally, a low-arginine diet combined with sodium benzoate therapy leads to a marked decrease in plasma N-acetyl-L-arginine concentrations. |